
13 No previous study has investigated risks of neurological disorders in children with more modestly depressed Apgar scores of 4-6 at 10 minutes or the risks of childhood neurological disorders across the full range of Apgar scores (that is, at each score value from 0 to 10).Ĭhanges in Apgar score values between one and five minutes are known to influence risks of cerebral palsy and epilepsy. This study showed that the risk of developing cerebral palsy was significantly higher in children with a 10 minute Apgar score between 0 and 3 compared with children who had a similar score at five minutes. 9 10 11 12 We are aware of only one previous study investigating risks associated with a low 10 minute Apgar score. Population based studies have shown that risks of cerebral palsy and epilepsy are increased in children with low Apgar scores, and a low Apgar score at five minutes confers a higher risk than a correspondingly low Apgar score at one minute. 1 However, several possible causes of low Apgar scores exist, such as perinatal asphyxia, congenital infections, maternal fever in labour, a diagnosis of chorioamnionitis, malformations, and preterm birth. A total score of 7-10 is considered “normal,” and a lower Apgar score indicates depressed vitality.
Apgar score skin#
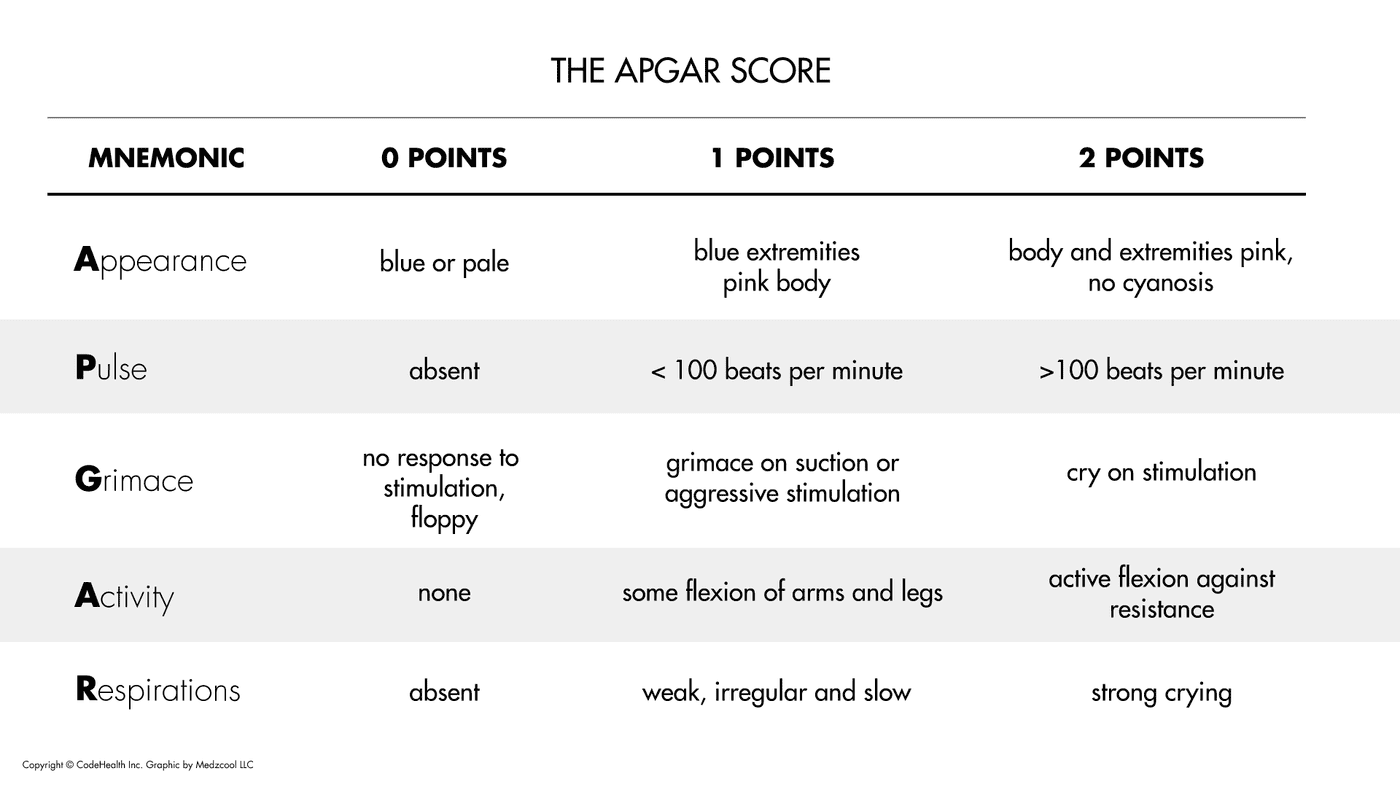
The score is based on measures of heart rate, respiratory effort, skin colour, muscle tone, and reflex irritability. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists propose use of an expanded Apgar score reporting form that accounts for concurrent resuscitative interventions.The Apgar score is a vitality index from 0 to 10 assigned to virtually every newborn infant at one, five, and 10 minutes after birth. There is a need for perinatal health care professionals to be consistent in assigning an Apgar score during a resuscitation.
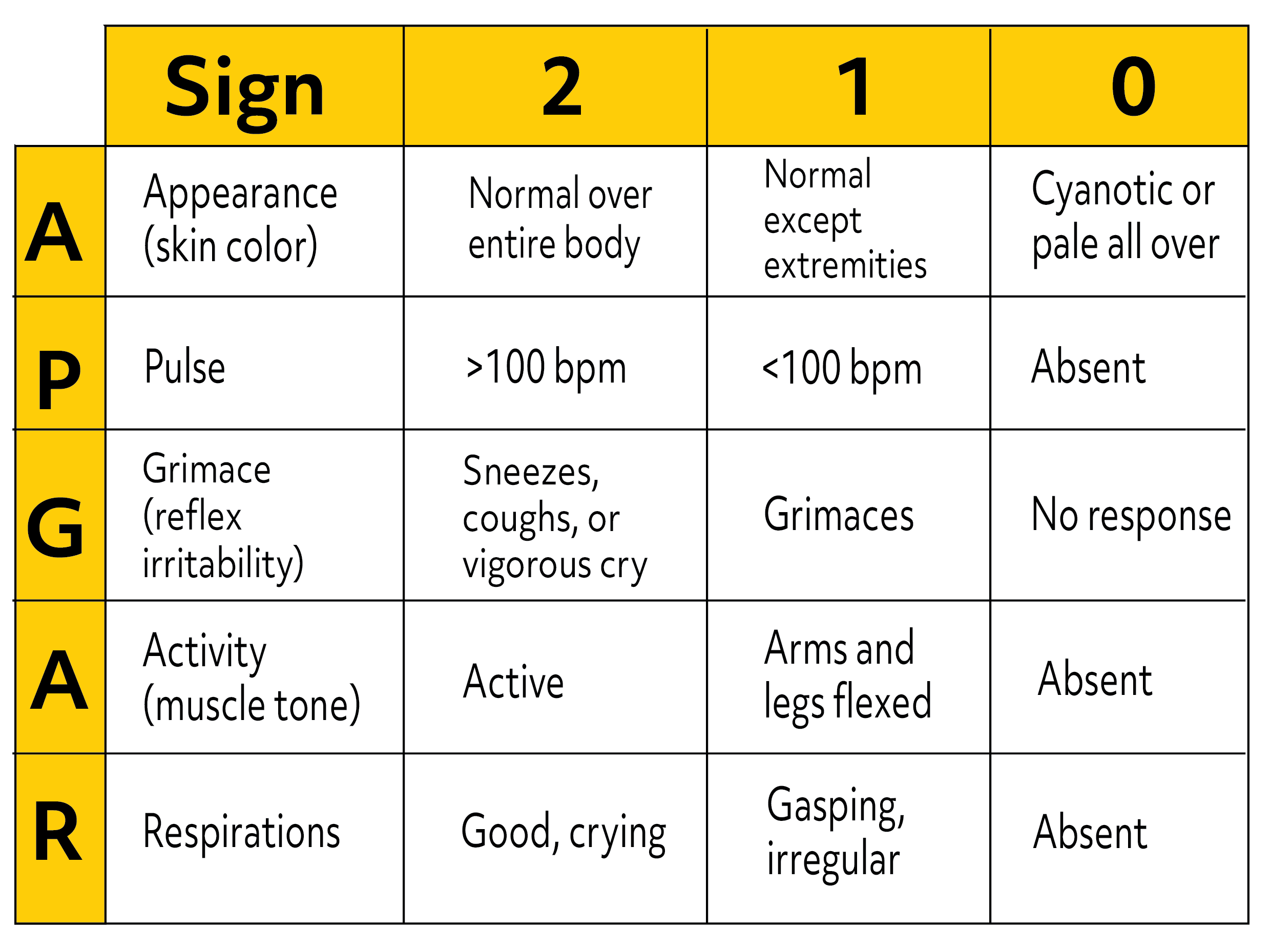
Resuscitative interventions modify the components of the Apgar score.

Low 1- and 5-minute Apgar scores alone are not conclusive markers of an acute intrapartum hypoxic event. The Apgar score is affected by gestational age, maternal medications, resuscitation, and cardiorespiratory and neurologic conditions. An Apgar score of 0 to 3 at 5 minutes may correlate with neonatal mortality but alone does not predict later neurologic dysfunction. It also provides a mechanism to record fetal-to-neonatal transition. The Apgar score describes the condition of the newborn infant immediately after birth 14 and, when properly applied, is a tool for standardized assessment. Descriptions such as hypercarbia, hypoxia, and metabolic, respiratory, or lactic acidemia are more precise for immediate assessment of the newborn infant and retrospective assessment of intrapartum management. Because the intrapartum disruption of uterine or fetal blood flow is rarely, if ever, absolute, asphyxia is an imprecise, general term.

Intrapartum asphyxia implies fetal hypercarbia and hypoxemia, which, if prolonged, will result in metabolic acidemia. Further, although the score is used widely in outcome studies, its inappropriate use has led to an erroneous definition of asphyxia. However, a persistently low Apgar score alone is not a specific indicator for intrapartum compromise. Neonatal Encephalopathy and Cerebral Palsy: Defining the Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology, 5 produced in 2003 by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists in collaboration with the American Academy of Pediatrics, lists an Apgar score of 0 to 3 beyond 5 minutes as one suggestive criterion for an intrapartum asphyxial insult. Previously, an Apgar score of 3 or less at 5 minutes was considered an essential requirement for the diagnosis of perinatal asphyxia. The purpose of this statement is to place the Apgar score in its proper perspective. Because there are no consistent data on the significance of the Apgar score in preterm infants, in this population the score should not be used for any purpose other than ongoing assessment in the delivery room. The Apgar score has been used inappropriately in term infants to predict specific neurologic outcome. The Apgar score continues to provide a convenient shorthand for reporting the status of the newborn infant and the response to resuscitation. The score is now reported at 1 and 5 minutes after birth. The Apgar score comprises 5 components: heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex irritability, and color, each of which is given a score of 0, 1, or 2. 2 This scoring system provided a standardized assessment for infants after delivery. 1 A second report evaluating a larger number of patients was published in 1958. In 1952, Dr Virginia Apgar devised a scoring system that was a rapid method of assessing the clinical status of the newborn infant at 1 minute of age and the need for prompt intervention to establish breathing.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
